Fish allergy is a type of food allergy that can appear in childhood, causing symptoms of varying severity after eating any type of fish or even inhaling its odor during cooking.
What is a fish allergy?
A fish allergy is an immune reaction that occurs when the body attacks certain proteins found in fish, such as parvalbumin.
This reaction leads to the release of chemicals that cause symptoms in the skin, digestive system, or respiratory system. The severity of symptoms varies from child to child depending on the type and quantity of fish consumed, and the child's sensitivity.
Causes of fish allergy in children
It occurs as a result of an overreaction of the immune system to various fish proteins. Common causes include:
- Genetic factors and a family history of allergies.
- Eating fish at an early age.
- Immature immune system.
- Exposure to fish proteins through the skin or breathing during cooking.
Symptoms of fish allergy in children
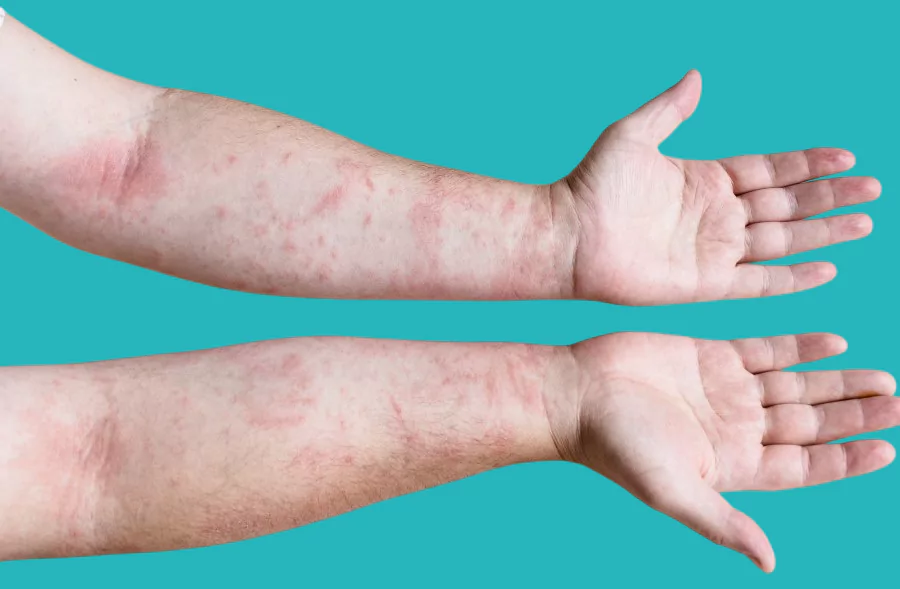
Symptoms usually appear within minutes of eating fish or inhaling its odor and include:
- Skin redness or severe itching.
- Swelling of the lips or eyelids.
- Vomiting or diarrhea.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- Dizziness or low blood pressure in severe cases.
Complications of Fish Allergy
Mild symptoms can develop into a severe allergic reaction known as angioedema. Possible complications include:
- Severe shortness of breath.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Loss of consciousness in emergency situations.
Diagnosis of Fish Allergy in Children
Diagnosis is based on the medical history and tests ordered by the doctor to confirm the allergy, such as:
- Skin allergy testing.
- Blood testing to detect antibodies.
- Avoid eating fish for a specific period and observe improvement.
Methods for Treating Fish Allergy in Children
There is no definitive cure for allergies, but they can be controlled by avoiding the cause. Treatment includes the following:
- Avoid eating all types of fish and fish products.
- Use antihistamines when symptoms occur.
- Prescribe epinephrine injections for emergency situations.
- Consult your doctor to determine protein-rich food alternatives.
Tips for Mothers Dealing with Fish Allergies

To prevent your child from allergic attacks, the following is recommended:
- Avoid fish in the home or while cooking.
- Read food ingredients carefully.
- Educate your child not to eat any seafood without supervision.
- Keep an adrenaline syringe handy for emergencies.
Can a child be allergic to just one type of fish?
Yes, some children may be allergic to a specific type, such as tuna or sardines, while tolerating other types. Therefore, the offending species must be accurately identified through medical examination.
Does a fish allergy go away over time?
It often does not go away like some other allergies, and in most cases, it lasts a lifetime. Therefore, it is essential to adhere to permanent avoidance.
Can a child develop an allergy to the smell of fish alone?
Yes, inhaling volatile fish proteins during cooking can cause respiratory symptoms in some severely allergic children.
Article Summary
Fish allergy is a condition that requires constant vigilance. Early detection and avoidance of triggers are the foundation of prevention. With proper medical care, your child can live a normal, safe life without complications.