Milk allergy is one of the most common food allergies in children. It usually appears in the early years of life when the immune system overreacts to cow's milk proteins.
What is a milk allergy?
A milk allergy is an overreaction to a protein in cow's milk or its derivatives, such as yogurt, cheese, and butter.
When a child consumes milk, their immune system treats the proteins as harmful substances, producing antibodies that trigger allergic symptoms on the skin, digestive system, or respiratory system.
It is one of the most common allergies that requires close medical monitoring to avoid complications.
Causes of Milk Allergies in Children
Allergies occur as a result of the immune system overreacting to certain proteins in milk, such as casein or whey. Common causes include:
- Genetic factors from one of the parents.
- Immature immune system.
- Consuming cow's milk at a very early age.
Symptoms of Milk Allergies in Children
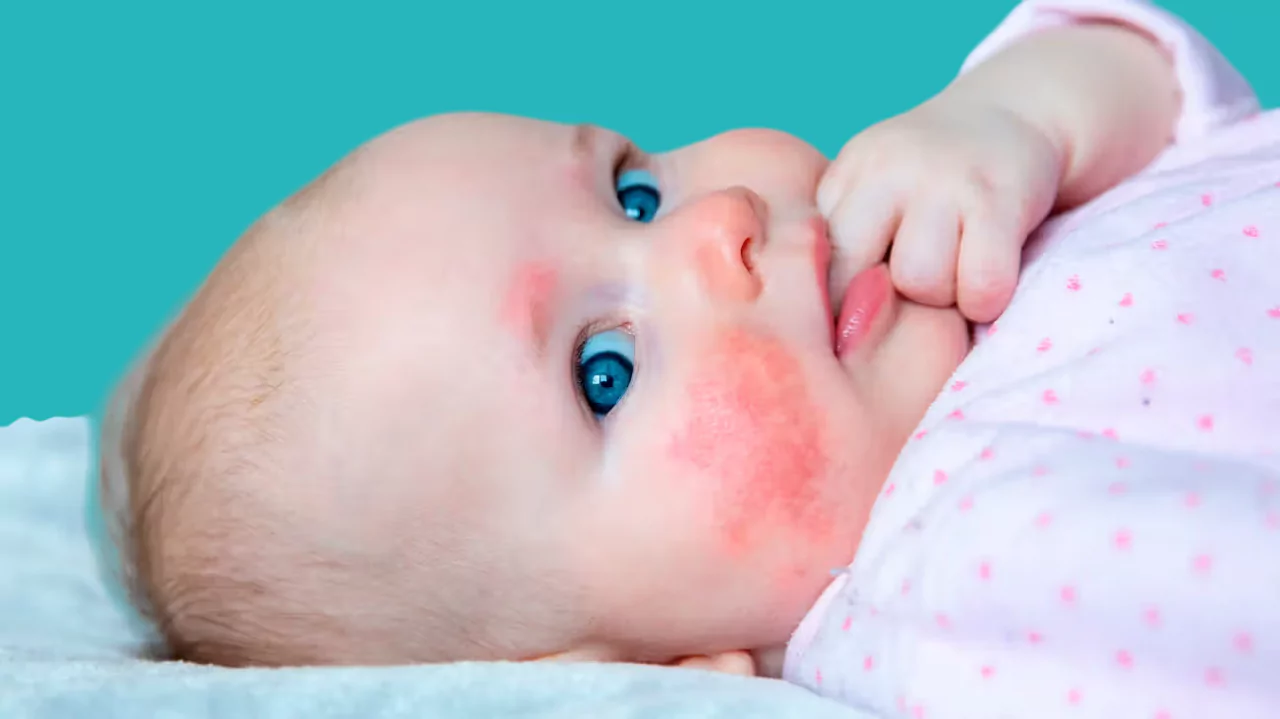
Symptoms appear within minutes or hours of consuming milk and include:
- Skin rash or reddening of the skin.
- Swelling of the face or lips.
- Cramps and abdominal bloating.
- Vomiting or diarrhea.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
Complications of a milk allergy
Sometimes the condition may develop into serious complications, such as:
- Severe allergic reaction.
- Loss of consciousness or low blood pressure.
- Respiratory disturbances.
Diagnosis of a milk allergy
The doctor diagnoses the condition based on symptoms and necessary tests, such as:
- Skin allergy testing.
- Blood test for antibodies.
- Milk abstinence test and monitoring for improvement.
Methods of treating milk allergy in children
Treatment relies on avoiding allergens and using safe alternatives, such as:
- Stop consuming cow's milk and dairy products.
- Use dairy-free infant formula.
- Administering antihistamines to relieve symptoms.
- Epidemiline injections in emergency situations.
Tips for mothers dealing with a milk allergy

To reduce allergic attacks, it is recommended to:
- Read food labels carefully.
- Replace milk with almond or oat milk.
- Regular follow-up with your doctor.
- Keep an emergency supply of adrenaline.
Does a milk allergy go away with time?
It may go away in some children as their immune systems mature, especially after the age of 3 to 5 years. However, this must be confirmed through medical tests before reintroducing milk.
What is the difference between a milk allergy and an intolerance?
An allergy results from an immune reaction to milk proteins, while an intolerance is a difficulty digesting lactose. The severity of symptoms varies between the two conditions.
Can a child develop an allergy to formula milk?
Yes, because most brands contain proteins from cow's milk. Therefore, the doctor may recommend special alternatives that are free of these proteins.
Article Summary
Milk allergy is a common condition in children, but it can be controlled with care and adherence to the doctor's instructions. With early diagnosis and regular follow-up, complications can be avoided and a healthier life can be achieved.