What is Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the blood and its ability to clot normally. Simply put, when a minor injury occurs, bleeding in a healthy person stops within minutes, but in a person with hemophilia, the bleeding may last much longer.
The reason is a deficiency or absence of one of the clotting proteins in the blood, which makes even minor injuries a real danger. The disease is often detected in childhood, but its symptoms can appear at any age.
What are the causes of Hemophilia?
There are several common causes of hemophilia, including:
- Genetic factor: It is usually inherited from a mother who carries the gene to her male child.
- New genetic mutation: It can occur in some cases without a family history.
- Deficiency of clotting factors: Such as factor VIII (Hemophilia A) or factor IX (Hemophilia B).
What are the common symptoms of Hemophilia?
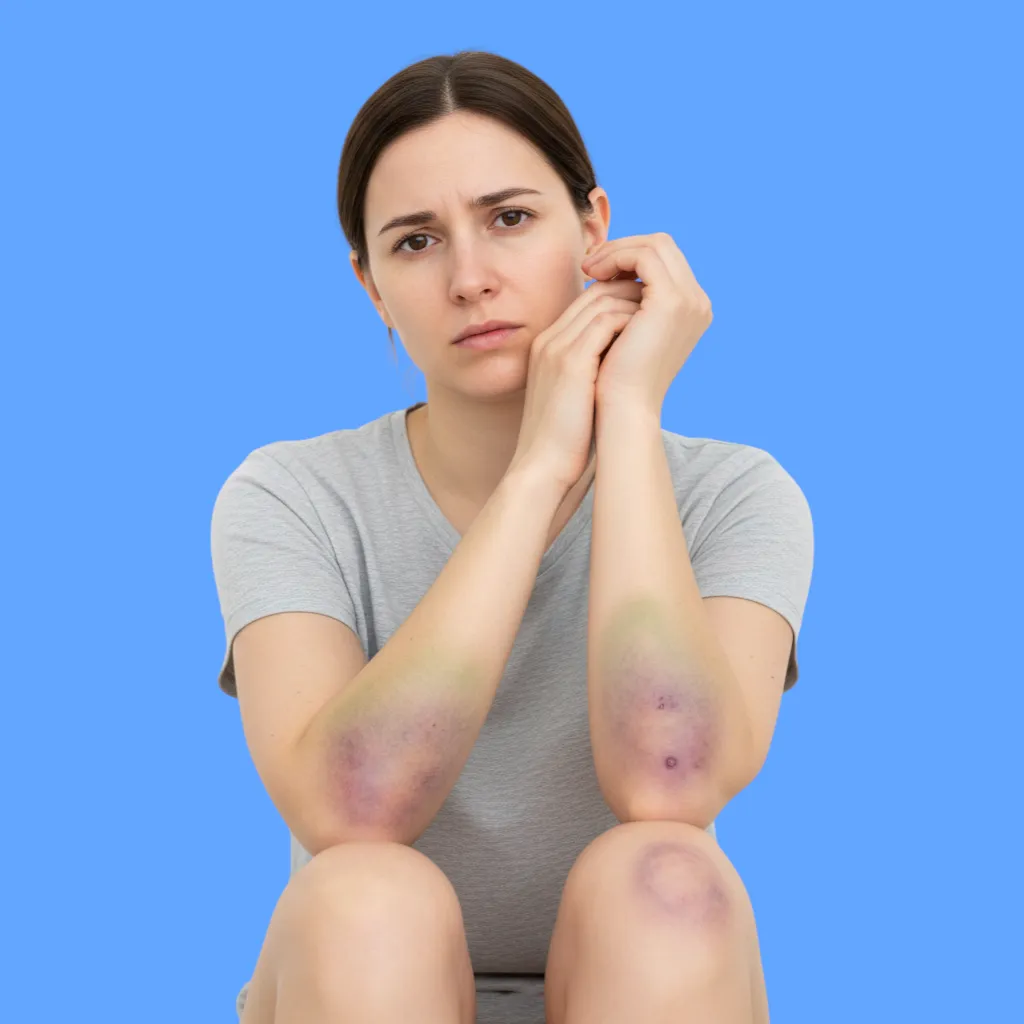
There are several common symptoms that a patient may experience, including:
- Frequent bleeding after minor injuries or cuts.
- Large bruises that appear easily on the skin.
- Internal bleeding in the joints causing pain and swelling.
- Bleeding after surgeries or tooth extractions.
- In severe cases, spontaneous bleeding without an obvious cause.
When should you see a doctor?
It is recommended to see a doctor immediately if any of the following occur:
- Bleeding that does not stop after a minor injury.
- Severe pain and swelling in the joints.
- Blood in urine or stool.
- Head bleeding after any injury, even if minor.
How is Hemophilia diagnosed?
The disease is diagnosed using several methods, including:
- Blood tests to measure clotting factor levels.
- Clotting time test to determine how quickly bleeding stops.
- Genetic testing to identify the type of mutation.
What are the treatment options for Hemophilia?
There are several treatment options for the disease, including:
- Replacement therapy: Injecting the missing clotting factors.
- Supportive medications: Such as Desmopressin to stimulate the production of some clotting factors.
- Preventive treatment: Regular doses to reduce bleeding episodes.
- Gene therapy: A modern technique to improve clotting factor production.
Can Hemophilia be cured?
Currently, there is no complete cure, but the disease can be well controlled with proper treatment. Gene therapy offers great hope for the future, but it is still under development.
What are the prevention tips for Hemophilia?
There are several tips to prevent complications, including:
- Avoid high-risk activities that may cause injuries.
- Use protective gear during sports.
- Consult a doctor before any surgery or tooth extraction.
- Stick to the prescribed preventive treatment.
What are the possible complications of Hemophilia?
Some complications may occur if the disease is left untreated, such as:
- Joint damage due to repeated bleeding.
- Severe internal bleeding in the brain or vital organs.
- Anemia caused by chronic bleeding.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hemophilia
Can a person with hemophilia play sports?
Yes, but safe sports should be chosen and violent activities avoided.
Can someone suddenly develop hemophilia?
No, it is a genetic disease present from birth.
Does a person with hemophilia need frequent blood transfusions?
Not always, only in cases of severe bleeding or surgery.
Can hemophilia be passed from father to children?
Rarely, it is usually passed from a mother who carries the gene.