Neonatal jaundice is one of the most common conditions affecting infants after birth and is most noticeable during the first few days of life.
Jaundice appears as a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes and is caused by high levels of bilirubin in the blood. In most cases, it is mild and temporary, but medical treatment is required to avoid complications.
What is neonatal jaundice
Jaundice in infants occurs when bilirubin, a substance produced by the breakdown of red blood cells, accumulates in the infant's body.
In the first few days, a newborn's liver cannot adequately process this excess bilirubin due to the liver's immature development. This causes yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Causes of jaundice in infants
Jaundice in newborns may be caused by natural or pathological factors, including:
- The child has favism.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Imperfect liver development or maturation.
- Increased breakdown of red blood cells.
- Difference in the mother's and infant's blood types.
- Digestive disorders. The baby does not receive enough breast milk.
- A prenatal infection such as toxoplasmosis, measles, or syphilis.
What are the symptoms of jaundice in newborns

Symptoms of jaundice in newborns are observed within the first 24 hours or two to three days after birth:
- Yellowing of the skin.
- Dark urine.
- Very light-colored stool.
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes.
- The baby is lethargic and sleepy.
- Weak breastfeeding and refuses milk.
Are there complications of jaundice in infants
Yes. If jaundice in infants is not treated promptly and the bilirubin level in the blood rises significantly, this can lead to serious complications.
One of the most important complications is kernicterus, which is damage to brain cells resulting from the accumulation of bilirubin in the brain, leading to delayed motor and mental development, hearing impairment, or cerebral palsy.
It can also lead to neurological disorders in rare cases. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are recommended to protect the baby from any permanent damage.
Types of Jaundice in Newborns
Jaundice in newborns is divided into several types, depending on the cause and time of onset:
- Natural jaundice.
- Pathological jaundice.
- Hemolytic jaundice.
- Breastfeeding jaundice.
When does jaundice in newborns disappear
Jaundice in newborns gradually disappears within a week or two after birth, especially if the cause is natural. However, in premature infants, jaundice may persist for three weeks or more.
In the case of breast-feeding jaundice, the level may remain elevated until the fourth or sixth week, but it is not dangerous as long as the infant is active and breastfeeding well.
If the jaundice persists for more than two weeks and the symptoms become more severe, a doctor should be consulted for the necessary tests and to avoid complications.
Diagnosis of Jaundice in Infants
Infant jaundice is diagnosed when the doctor observes yellowing of the infant's skin and eyes and measures the bilirubin level in the blood.
Additional tests may be performed, such as blood typing, liver function tests, and red blood cell counts, to determine the type and severity of jaundice.
Treatment of Jaundice in Newborns
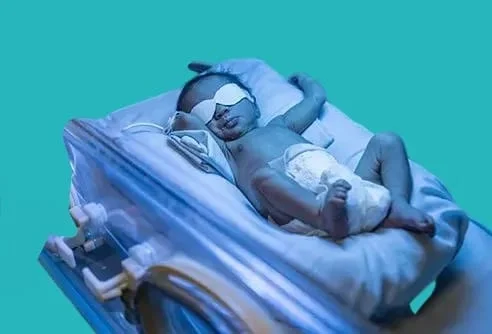
Jaundice in newborns often disappears within two weeks with regular monitoring, but the following are recommended:
- Regular breastfeeding.
- Blue light therapy.
- Partial exchange transfusion.
- Exposing the baby to indirect daylight.
How to Prevent Jaundice in Newborns
It is recommended to follow the following instructions to prevent jaundice in newborns:
- Check the blood typing of the baby and mother.
- Monitoring the baby immediately after birth.
- Ensure regular breastfeeding.
Article Summary
Jaundice in newborns is one of the most common conditions, appearing as a yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin in the blood.
Jaundice is usually a mild condition that resolves after two weeks of treatment and rest, but in some cases, serious complications may occur and require immediate treatment.
Therefore, parents should examine and monitor their infant daily during the first days after birth and consult a doctor if they notice any yellowing, lethargy, or drowsiness in the child.