Asthma is a common chronic disease in children. It is one of the most common reasons for visits to the doctor during childhood. It can significantly impact a child's quality of life if not properly controlled, as it causes shortness of breath and severe coughing.
What is Asthma in Children?
Asthma in children is a chronic respiratory disease that affects the airways, causing them to narrow, become inflamed, and produce excess mucus, which impedes breathing. Asthma often occurs in the form of recurrent episodes of shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing, which worsen at night, disrupting sleep, and during physical exertion.
Causes of Asthma in Children

There are several factors that cause asthma in children, including:
- Genetic factors, i.e., a family history of asthma or allergies.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to cigarette smoke or air pollution.
- Allergies to dust, pets, and mold.
- Recurrent respiratory infections, especially at an early age.
- Physical activity, as asthma is sometimes triggered after exercise.
Symptoms that indicate that a child has asthma
Symptoms vary from one child to another and may include:
- A persistent cough, especially at night or while playing.
- Wheezing or wheezing.
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest pain.
- Easy fatigue during physical activity.
Methods for diagnosing asthma in children
The process of diagnosing a child with asthma depends on:
- A medical history, including the frequency and timing of symptoms.
- A physical examination to listen to breathing sounds.
- Breathing tests, such as spirometry in older children.
- Allergy tests to detect allergens.
- The child's response to medications is sometimes used to confirm the diagnosis.
Possible complications of untreated asthma
If asthma is not well controlled, complications may occur, such as:
- Severe asthma attacks requiring emergency care.
- Impaired physical growth or physical activity.
- Sleep disturbances due to nighttime symptoms.
- Long-term lung problems.
Medications Used to Treat Asthma in Children
Medications used to treat asthma are divided into two types:
- Long-term control medications, inhaled corticosteroids such as budesonide or fluticasone.
- Quick-relief medications such as albuterol (Ventolin), are used during an attack to open the airways.
Very Important Warning: Please do not take any medication without consulting your doctor.
Methods for Treating Asthma in Children
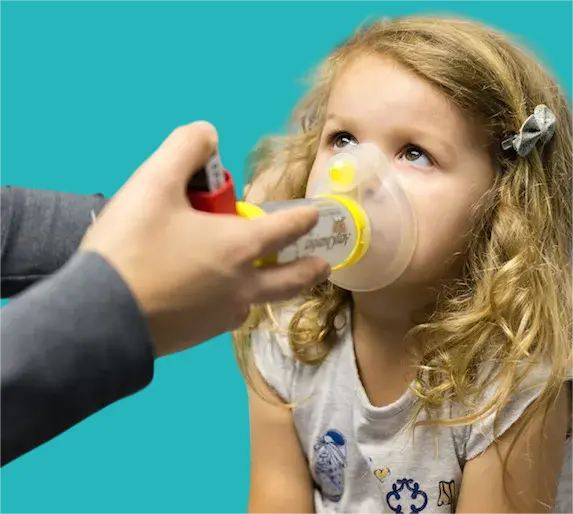
There are several methods for treating children with asthma, including:
- Using inhalers and nebulizers as directed by your doctor.
- Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers.
- Immunotherapy in some cases of allergy.
- A written management plan that explains to parents how to deal with symptoms and attacks.
- Regular doctor visits to monitor the condition and adjust treatment accordingly.
Can asthma attacks be prevented?
Children can be prevented from asthma attacks by:
- Avoiding allergens such as dust or animal dander.
- Maintaining a clean, smoke-free environment.
- Monitoring the condition with a doctor and taking medications regularly.
- Vaccinate your child against influenza and seasonal infections.
- Ensure that your child uses their inhaler correctly.
Can asthma affect your child's life?
Yes, it can affect your child's life if left uncontrolled, as it may limit physical activity, cause sleep disturbances, or interfere with academic concentration. However, if treated properly, your child can lead a completely normal life.
What is the role of parents in managing asthma?
Parents play a very important role in managing asthma, helping improve their child's condition by:
- Educating them about the disease and taking it seriously.
- Ensuring that your child takes their medication regularly.
- Avoiding exposing your child to environmental triggers.
- Maintaining and following a written treatment plan.
- Responding immediately to serious symptoms.
Article Summary
Asthma in children is a chronic respiratory disease that causes breathing difficulties and a persistent cough, especially at night or during exertion. However, it can be effectively controlled if properly diagnosed and treated. Its causes vary between genetic and environmental factors, and its symptoms include wheezing and shortness of breath.
Good awareness, adherence to treatment, and avoidance of triggers play a key role in protecting children from complications and enabling them to live a healthy and active life.