Sickle cell anemia is a chronic disease that affects the blood and causes various health problems. It is passed down genetically from parents to children.
What is sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anemia is a type of hereditary anemia caused by a change in the shape of red blood cells from their normal round shape to a crescent shape that impedes blood flow.
Causes of sickle cell anemia
This disease is primarily caused by genetic factors, and there are several main causes, including:
- The transmission of the causative gene from one or both parents.
- A genetic mutation in the hemoglobin.
- The risk of infection is increased if both parents are carriers of the disease.
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia in women

Anemia appears in childhood, and symptoms are often recurring and affect quality of life. The most important symptoms include:
- Recurring bouts of pain in the bones and joints.
- Fatigue and a constant feeling of tiredness.
- Pale skin and poor growth.
- Frequent infections.
- Vision problems and swelling of the extremities.
Methods of treating sickle cell anemia
There is no definitive cure for this disease, but symptoms can be controlled and complications reduced through several methods, the most important of which are:
- The use of certain medications to reduce pain attacks.
- Regular blood transfusions to improve oxygen levels.
- Bone marrow transplantation in some cases.
- Adherence to a healthy lifestyle and avoiding dehydration.
Methods for diagnosing sickle cell anemia in women
Diagnosis of the disease relies on a set of medical tests, the most important of which are:
- Complete blood count.
- Examination of the shape of red blood cells under a microscope.
- Sickled hemoglobin test.
- Genetic tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Medications for Sickle Cell Anemia
There are several medication options that may help patients control symptoms and reduce complications, including:
- Hydroxyurea to reduce the number of attacks.
- Antibiotics and vaccines to prevent infection.
- Pain relievers as recommended by a doctor.
Impact of the disease on pregnancy
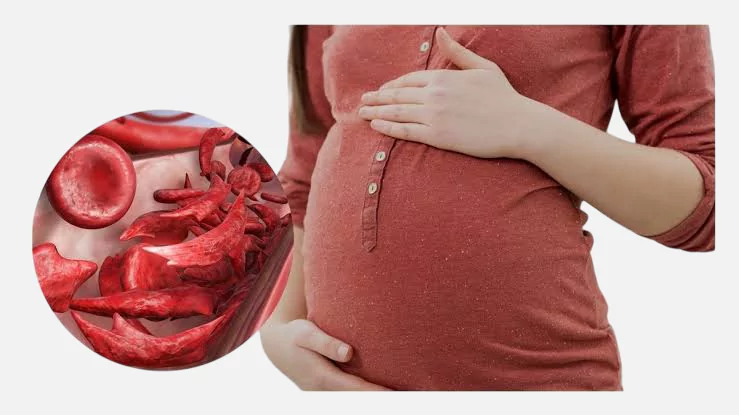
Sickle cell anemia in women can pose a risk to the pregnant woman and the fetus, increasing the risk of:
- Premature birth.
- Miscarriage.
- Preeclampsia.
- Low birth weight.
Is sickle cell anemia contagious?
No, sickle cell anemia is a genetic disease that is passed on through genes and is not contagious.
Is sickle cell anemia completely curable?
There is currently no cure, but a bone marrow transplant may offer hope for some cases, while symptoms can be controlled with medication and medical care.
Summary of the symptoms of sickle cell anemia in women and their impact on pregnancy
Sickle cell anemia in women is a hereditary blood disease that affects the shape of red blood cells and causes symptoms such as fatigue, pain attacks, and serious complications to organs and pregnancy.
It can be controlled through medication, blood transfusions, and infection prevention. Premarital genetic testing is also an important step in preventing the disease from being passed on to future generations.