Uterine fibroids are one of the most common health problems among women of reproductive age. They are often benign and non-cancerous. Their symptoms vary from woman to woman, and they may go undetected except during routine examinations. Hormones and genetic factors play a major role in their development.
What are uterine fibroids?
A uterine fibroid is an abnormal growth in the uterus. It is often benign, meaning non-cancerous. They are muscular masses that grow in the uterine wall and may be very small or large enough to affect the shape and size of the uterus.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
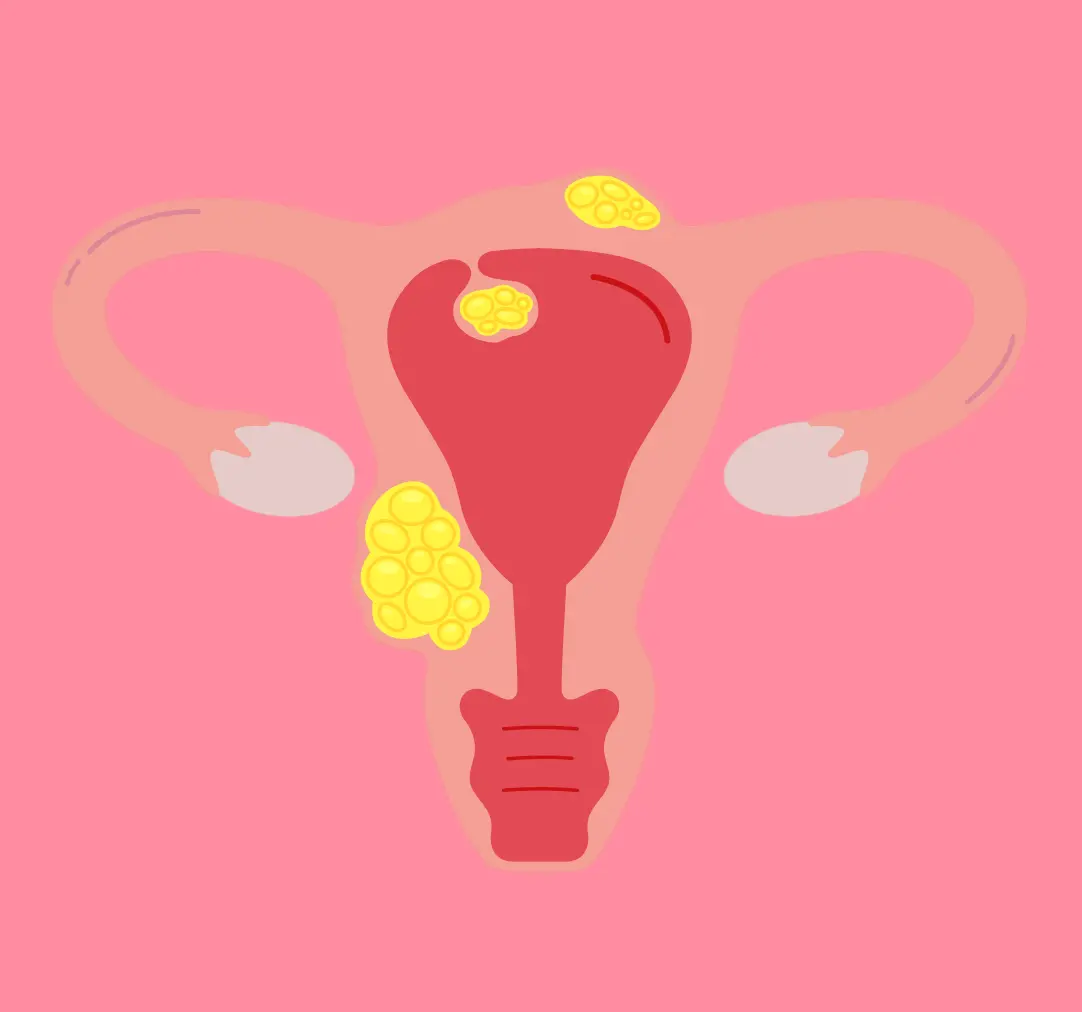
Several factors cause uterine fibroids, including:
- Increases in hormones, especially estrogen and progesterone, which stimulate the growth of the uterine lining.
- Genetic factors, meaning a family history of fibroids.
- Obesity may increase the risk.
- Early menstruation may be associated with an increased risk.
Symptoms of Uterine Tumors
Some women do not experience symptoms of uterine tumors, but several symptoms may occur, including:
- Heavy or abnormal bleeding during menstruation.
- Pelvic or back pain.
- Frequent urination.
- Constipation.
- Abdominal swelling.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Pelvic pressure.
How are uterine tumors diagnosed?
Uterine tumors are diagnosed using several methods, including:
- Clinical examination.
- Vaginal or abdominal ultrasound.
- MRI.
- Hysteroscopy or contrast imaging.
- Blood tests.
Complications of uterine tumors
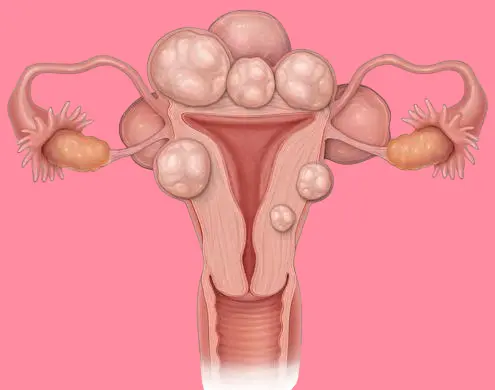
Some complications may occur as a result of uterine tumors, including:
- Anemia due to heavy bleeding.
- Pregnancy and fertility problems.
- Chronic pain.
- Miscarriage or premature birth.
Medications Used to Treat Tumors
There are many medications that treat uterine tumors, including:
- Antihormonal medications to reduce tumor size.
- Birth control pills to regulate bleeding.
- Hormonal IUDs to reduce uterine bleeding.
Methods of Treating Uterine Tumors
Treatment methods depend on the symptoms and extent of the disease, including:
- Drug therapy.
- Surgical treatment, such as removing the tumor alone or hysterectomy.
- Non-surgical treatment, such as focused ultrasound (FUS).
Preventive methods to reduce the risk of developing uterine tumors
It is not possible to completely prevent them, but there are ways to reduce the likelihood of developing them, including:
- Regular checkups.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Monitoring your menstrual cycle to detect changes in blood volume.
- Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Avoid smoking and alcoholic beverages.
Do uterine tumors affect pregnancy?
Yes, in some cases, they can prevent implantation or lead to recurrent miscarriages.
What is the difference between benign and malignant uterine tumors?
A benign uterine tumor is non-cancerous, does not spread to other organs, and may not require treatment.
A malignant uterine tumor, on the other hand, is cancerous and may spread to the lungs or liver, requiring treatment such as surgery or chemotherapy.
Summary of the Causes of Uterine Tumors and Methods of Prevention
Uterine tumors are growths that appear in the uterus, often known as fibroids. They vary in size and location and may not cause symptoms, but in some cases, they cause heavy bleeding and pelvic pain. The risk of developing them is highest in women between the ages of thirty and fifty. To prevent them, it is important to maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and seek regular medical care, especially if symptoms or a family history are present.