what is scabies?
scabies is a contagious skin condition that spreads easily between people and causes intense itching due to the body's reaction to tiny mites burrowing into the skin.
it often appears in places with frequent gatherings or direct contact and significantly affects the patient's quality of life.
causes of scabies
the most common causes of scabies include:
- direct physical contact with an infected person.
- using personal items of an infected person such as towels or clothes.
- sleeping in the same bed with someone who has the infection.
- weakened immunity or chronic illnesses.
- being in crowded places like schools or care homes.
- poor personal hygiene.
- sharing tools in workplaces or communal housing.
- transmission from infected animals in rare cases.
symptoms of scabies
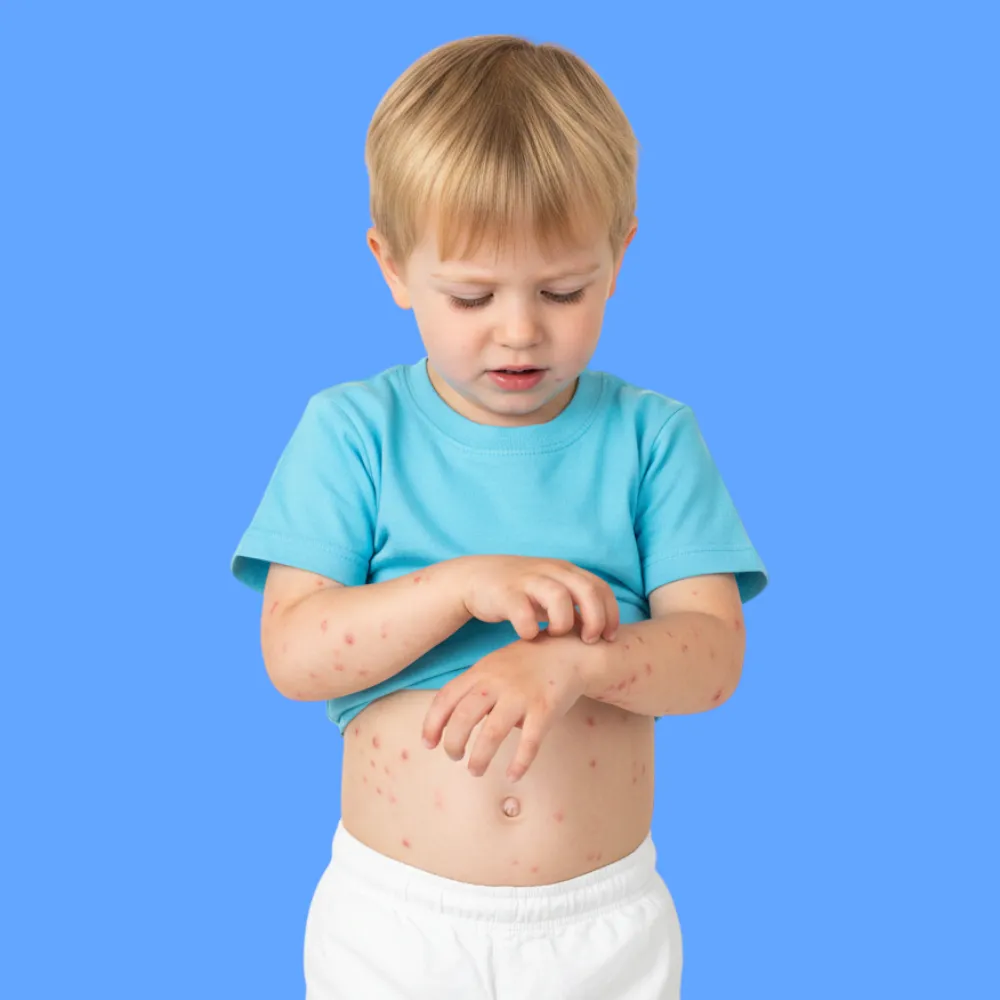
common symptoms a patient may experience include:
- intense itching that worsens at night.
- appearance of skin rash or small blisters.
- thin lines on the skin resembling tunnels.
- sores caused by continuous scratching.
- redness and swelling in certain areas.
- skin peeling or dryness.
- sensation of heat or tingling in the skin.
- symptoms spreading to multiple body areas.
when to see a doctor?
it is advised to consult a doctor promptly if any of the following occur:
- persistent itching for more than a week without improvement.
- appearance of sores or skin infections.
- symptoms spreading to other household members.
- ineffectiveness of home treatments.
- symptoms in sensitive areas like the face or genitals.
- fatigue or fever accompanying the symptoms.
- worsening condition despite medication.
- emergence of unusual new symptoms.
treatment of scabies
several methods are available to treat scabies, including:
- using topical creams that fight mites.
- taking oral medications as prescribed by a doctor.
- applying natural remedies like tea tree oil.
- washing clothes and bedding in hot water.
- avoiding direct contact with others.
- using products that soothe itching.
- thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting the home.
- following up with the doctor to assess treatment response.
diagnosis of scabies
scabies is diagnosed through a clinical examination of the skin, where the doctor looks for distinctive signs such as rash and persistent itching, especially in hard to reach areas.
in some cases, a small skin scraping is performed using a precise tool, and the sample is examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of mites, helping ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
prevention tips
recommended ways to prevent infection include:
- avoid sharing clothes or towels with others.
- wash hands regularly with soap and water.
- clean bedding and linens periodically.
- maintain daily personal hygiene.
- avoid direct contact with infected individuals.
- use disinfectants in public places.
- ventilate the home properly.
- monitor for early skin symptoms.
frequently asked questions
is scabies contagious?
yes, it spreads easily from person to person.
can scabies be treated at home?
in some cases yes, but it's better to consult a doctor.
how long does scabies treatment take?
usually one to two weeks depending on the case.
does scabies affect children?
yes, and it may be more severe in them.
article summary
scabies is a contagious skin disease that causes intense itching due to mites under the skin, it spreads easily through contact, is diagnosed clinically or microscopically, and can be treated with creams or oral medications. prevention relies on hygiene and avoiding direct contact with infected individuals.