Preeclampsia is a serious complication that can affect women during pregnancy. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine after the twentieth week of pregnancy.
Although it does not occur in all pregnant women, neglecting to monitor it can cause serious health problems for the mother and fetus. Therefore, awareness of its causes, symptoms, and treatment methods is an essential step in protecting the health of the mother and fetus.
What is preeclampsia
It is a disorder that occurs after the twentieth week of pregnancy. It is not toxicity in the literal sense, but rather a medical condition related to pregnancy that affects the health of the mother and fetus if not treated early.
Symptoms of preeclampsia

- Reduced urination.
- Vision disturbances.
- Persistent nausea and vomiting.
- Severe and persistent headache.
- Protein in the urine.
- Significantly high blood pressure.
- Swelling of the face, feet, and hands.
- Upper abdominal pain.
- Sudden and rapid weight gain due to fluid retention.
What are the types of preeclampsia
- The types of preeclampsia vary according to their severity and onset.
- Mild preeclampsia. Severe preeclampsia.
- Early-onset preeclampsia (preeclampsia).
- Late-onset preeclampsia.
- Convulsions (eclampsia).
What are the causes of preeclampsia
The exact causes are unknown, but there are factors that play a role in its development, such as:
- First pregnancy.
- Twin pregnancy.
- Genetic factors.
- High maternal blood pressure.
- A family history of preeclampsia.
- Problems with placental formation or growth.
- Maternal diabetes or kidney disease.
- Impaired maternal immune system during pregnancy.
- A blood vessel disorder leading to poor blood flow to the placenta.
How is preeclampsia diagnosed
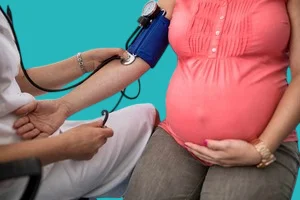
Diagnosis relies on measuring the mother's blood pressure, performing a urine test to detect protein, and performing tests to monitor liver and kidney function, platelet count, and, most importantly, performing fetal tests, such as an ultrasound to monitor fetal growth and check blood flow to the placenta.
Complications of Preeclampsia for the Mother and Fetus
Complications of preeclampsia for the mother include:
- Kidney or liver failure.
- It may be life-threatening for the mother.
- Eclampsia.
- HELLP syndrome.
- Bleeding and placental abruption.
Complications for the fetus include:
- Premature birth.
- Low birth weight.
- Slow or stunted fetal growth in the uterus.
- Low oxygen and nutrient supply to the placenta.
How can preeclampsia be prevented
To prevent preeclampsia, blood pressure and urine tests should be monitored regularly during pregnancy. A healthy diet should be followed, excess salt intake reduced, and a healthy weight maintained before and during pregnancy should be maintained.
Close follow-up with your doctor is also recommended, especially if there are risk factors such as the mother's chronic illnesses. It is also recommended to take supplements such as calcium or aspirin in preventive doses if recommended by your doctor.
Medications for Treating Preeclampsia
- Medications to Lower Blood Pressure
- Anticonvulsant Medications
- Injections to prevent seizures.
- Steroid injections.
Does preeclampsia lead to premature birth
Yes, preeclampsia can cause premature birth, especially if the condition is severe and threatens the life of the mother and fetus, or if it affects the placenta and reduces the flow of blood and nutrients to the fetus.
This leads to delayed growth or weakness of the fetus, resulting in premature birth. This is a safe solution for doctors, along with steroid injections to stimulate fetal lung development.
Methods for controlling preeclampsia
- Relatively resting the mother.
- Reducing salt in the diet.
- Fetal monitoring with ultrasound.
- Committing to a healthy diet.
- Close monitoring during pregnancy.
- Taking anticonvulsant medications.
- Continuous blood pressure monitoring.
Summary of preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure with protein in the urine after the twentieth week. It causes headaches, swelling, and blurred vision, which can lead to serious complications.
Therefore, it is important to follow your doctor's instructions carefully to control preeclampsia and to ensure regular follow-up during pregnancy.